A new study shows why fine sediments in rivers are not simply proportional to the water flow across the United States.
By Simone Bizzi
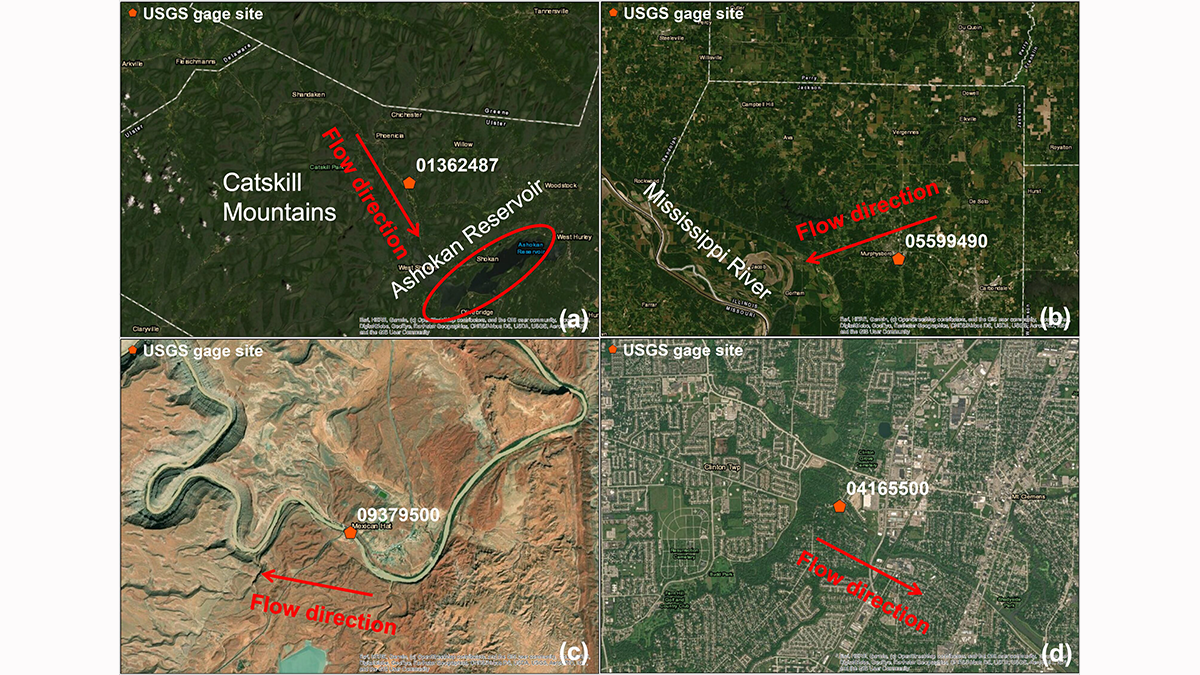
Examples from the United States of four different basin conditions that create rivers with distinct turbidity–water flow relationships: (a) Beaver Kill, New York; (b) Big Muddy River near mouth entering the Mississippi River, Illinois; (c) San Juan River, Utah; and (d) Clinton River, Michigan. Credit: Wang and Steins [2022], Figure 3
The amount of fine sediments and associated turbidity generated by flowing water in a basin do not simply increase or decrease with the river flow but depend upon several factors, such as land use, geology, precipitation, and human activities. However, there are few studies that have explored how fine sediment transport dynamics correlate with streamflow and other basin features across the continental United States.
Wang and Steinschneider [2022] studied this relationship exhaustively and show how the proportion of river turbidity for a given flow is a function of the season, the shape of a river network, and the soil properties. The results have important implications to better understand the potential sediment transport dynamicity in a specific region. These valuable findings can also be used for improving the sediment monitoring strategy in the United States and potentially worldwide.
Citation: Wang, K., & Steinschneider, S. (2022). Characterization of multi-scale fluvial suspended sediment transport dynamics across the United States using turbidity and dynamic regression. Water Resources Research, 58, e2021WR031863. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR031863
—Simone Bizzi, Associate Editor, Water Resources Research
(Source: https://eos.org/editor-highlights/disentangling-river-water-turbidity-and-its-flow)

